Body Mass Index (BMI) has become a familiar term in our health-conscious society. It’s a calculation used by healthcare professionals to assess an individual’s weight status and potential health risks. However, many people are unsure about the true meaning and accuracy of BMI.
BMI is more than just a number – it provides valuable insights into our well-being. In this article, we’ll demystify BMI by exploring what it really means, how it’s calculated, and its limitations. Understanding BMI can help us gain a deeper understanding of our overall health and make informed decisions about our lifestyle choices.
What is Body Mass Index (BMI)?
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a metric that relates a person’s weight to their height, providing a rough estimate of body fat levels and potential weight-related health issues. While convenient and inexpensive, BMI has limitations as it doesn’t account for factors like muscle mass, bone density, body composition, or where someone carries their weight. Individual characteristics like gender, age, and ethnicity can also impact the accuracy of BMI readings.
Despite its limitations, BMI remains a valuable initial screening tool in healthcare settings. It helps identify people potentially at risk of weight-related health problems. BMI scores typically fall into categories like underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obese, each with different associated health implications.
While imperfect, BMI gives a general sense of someone’s weight status and flags cases where more detailed body composition assessments may be warranted. Used responsibly alongside other health indicators, it can be a helpful first-line data point for weight management and disease prevention efforts.
How to Calculate BMI?
BMI can be calculated by measuring a person’s height and weight.
Using Imperial Units:
- To calculate BMI using imperial units, follow this method: BMI = lbs x 703/in2.
- Simply multiply your weight in pounds (lbs) by 703. Then divide the result by your height in inches, squared (in2).
Using Metric Units:
- For metric units, the formula is: BMI = kg/m2.
- Divide your weight in kilograms (kg) by the square of your height in meters (m2).
If you prefer not to perform the calculations yourself, you can easily find out your BMI using a free online BMI calculator. Click here to find your BMI now. Afterward, refer to the chart below to determine whether your BMI falls within a healthy range or not.
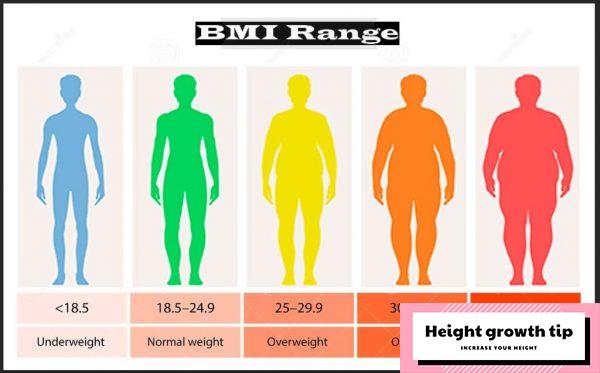
| BMI | Weight state |
| Under 18.5 | Underweight |
| 18.5 – 24.9 | healthy weight |
| 25.0 – 29.9 | Obesity |
| Over 30.0 | Fat |
How does your Body Mass Index (BMI) impact your health?
Your body mass index (BMI) is a measure that combines your weight and height. Numerous studies have shown that excess weight substantially increases your risk for serious medical problems like type 2 diabetes, heart disease, stroke, certain cancers, osteoarthritis, sleep apnea, and fatty liver disease. Excess fat disrupts the body’s biochemical processes, dysregulating hormones, raising inflammation, and clogging organs and blood vessels.
On the other hand, maintaining a normal BMI through balanced eating and exercise lowers the risk for these chronic conditions while boosting energy, mobility, and overall quality of life. BMI doesn’t account for muscle mass or body composition, and health implications can vary between individuals. However, maintaining a healthy weight is one of the smartest investments you can make for your future well-being
Pros and Cons of BMI (Body Mass Index)
Pros:
- Universally accepted metric for assessing obesity across individuals and populations.
- Cost-effective screening tool, especially for larger population groups.
- Provides an overall risk assessment for obesity-related diseases when combined with other measures.
Cons:
- Does not account for body composition – can misclassify muscular or overfat individuals.
- May be inaccurate for certain demographics like athletes, elderly, etc.
- Fails to distinguish between different types of fat (visceral vs subcutaneous).
In summary, BMI is a simple, standardized and inexpensive metric, but has limitations in not considering muscle mass, fat distribution or demographics. It works best when supplemented with additional health markers for a more comprehensive assessment.
What Steps Can You Take to Maintain a Healthy BMI?
For Those Underweight (BMI <18.5):
- Eat a nutrient-dense diet with enough calories
- Don’t skip meals – establish a regular eating routine
- Work with a professional on a healthy weight gain plan with diet and strength training
- Stay active with a mix of cardio, strength, and flexibility exercises
- Limit sugary/processed foods, smoking, and excessive alcohol
For Those at a Normal Weight (BMI 18.5-24.9):
- Maintain balanced eating and regular exercise habits
- Get regular medical checkups
For Those Overweight/Obese (BMI >25):
- Adopt a calorie-controlled, nutrient-rich diet
- Prioritize exercise with cardio and strength training
- Build sustainable habits like portion control and managing eating triggers
- Consider guidance from doctors, nutritionists or weight loss programs
Remember, factors like muscle mass and health conditions impact BMI. The goal is overall wellness, not just the number. Work closely with your healthcare team for a personalized, safe approach to reaching and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Related post: Does Volleyball Increase Height?

