Are you curious about where your current weight falls on the spectrum of health? Is it classified as thin, healthy, overweight, or obese? The key to unlocking this information lies in a simple yet powerful calculation known as the Body Mass Index (BMI).
BMI is a valuable tool for not only assessing your weight but also managing it effectively. It serves as a crucial step in preventing excessive weight gain and reducing the associated health risks. This calculation is universally applicable, suitable for both adult men and women aged 18 and above, providing a reliable indicator of overall health status. However, it’s important to recognize that BMI is not suitable for everyone, including pregnant women, competitive athletes, professional bodybuilders, and the elderly, who may have unique health considerations. Additionally, it’s worth noting that BMI thresholds can differ depending on your country of residence.
Understanding and calculating your BMI is a fundamental aspect of maintaining a healthy and well-balanced body. Armed with this knowledge, you can make informed decisions regarding your diet and portion sizes, helping you align your eating habits with your weight-related goals, whether that involves gaining or losing weight to achieve optimal health. So, let’s delve deeper into the world of BMI and how it can be your ally in your journey towards a healthier you.
What is the formula for calculating BMI?
The Body Mass Index (BMI), a metric employed by nutritionists to assess an individual’s weight status, serves as a fundamental tool in evaluating whether someone falls into the categories of being underweight, having a normal weight, or being overweight, all based on their body weight. The origins of BMI trace back to 1832 when a Belgian scientist first introduced the concept.
The formula for computing BMI is simple and necessitates only two pieces of information: height and weight. Here is the formula for calculation:
BMI = weight (in kilograms) / height (in meters)²
It’s essential to recognize that BMI, while a valuable measure, does not offer a comprehensive assessment of body fatness or overall health. Factors such as muscle mass, body shape, and age also play pivotal roles in an individual’s health profile. Nonetheless, BMI serves as a valuable tool for individuals to assess their weight status and make informed decisions to enhance their overall well-being.
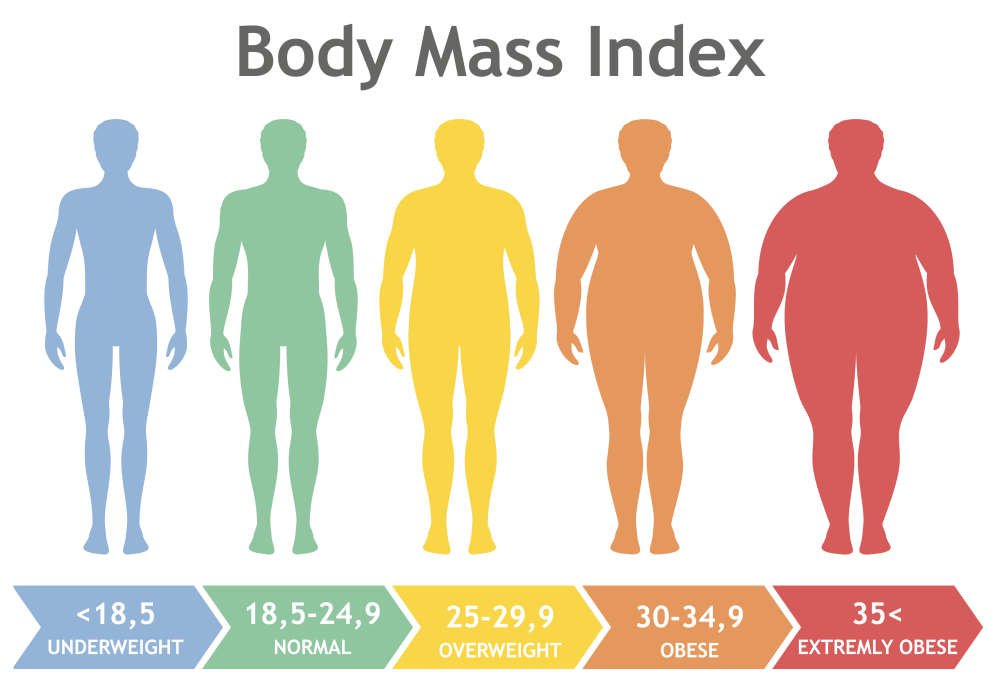
Classification of weight according to BMI
Based on BMI, you will know which group you belong to. There are 4 weight levels including: underweight (thin) – normal weight – overweight (slightly fat) – obese. Whether you’re underweight or overweight is cause for concern, especially when it’s far above the normal weight norm.
The image below is a chart of BMI classified from underweight to obese based on the classification scale of WHO – World Health Organization.
According to the classification table, the BMI that is considered normal for Vietnamese people will fall between 18.5 – 24.9. Less than 18.5 means you are underweight, and higher than 24.9 means you are overweight.
Besides, a different way to help you quickly calculate the normal weight index compared to height according to the formula:
| Ideal weight | [Odd number of height (in cm) x9] / 10 |
| Maximum weight | By odd number of height (in cm) |
| Minimum weight | [Odd number of height (in cm) x8] / 10 |
For example: Your height is 165cm then:
- Ideal weight = 65 x 9 : 10 = 58.5kg
- Maximum weight: 65kg
- Minimum weight = 65 x 8 : 10 = 52kg
This is a quick way to help you easily determine your normal weight limit. Of course, if your weight is less than the minimum weight, you are underweight, if it is higher, you are overweight.
The Significance of Maintaining a Healthy BMI
Maintaining a healthy Body Mass Index (BMI) is not just a matter of aesthetics; it is a fundamental pillar of overall well-being. The impact of a balanced BMI extends far beyond mere appearances, with robust scientific evidence illuminating its pivotal role in reducing the susceptibility to a plethora of chronic health conditions. The relationship between BMI and health is complex, yet its implications are crystal clear: an elevated BMI is often synonymous with a heightened risk of contracting chronic diseases, such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and specific forms of cancer. Conversely, a BMI within the healthy range is consistently linked to superior cardiovascular health, increased physical mobility, and an elevated standard of living.
Exploring the Multifaceted Determinants of BMI
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a multifaceted metric, influenced by a myriad of factors. Understanding these determinants is essential for gaining insights into one’s weight status and overall health. Let’s delve deeper into the various key factors that play a pivotal role in shaping an individual’s BMI:
- Dietary Habits: The composition of one’s diet, portion sizes, and overall diet quality significantly impact BMI. Maintaining a balanced, nutritious diet that encompasses a variety of food groups is paramount for sustaining a healthy BMI.
- Physical Activity: Regular physical activity and exercise are instrumental in weight management and BMI regulation. Sedentary lifestyles are often associated with higher BMIs, whereas an active lifestyle can aid in BMI maintenance or reduction.
- Genetics: Genetic predisposition plays a substantial role in an individual’s tendency to gain or lose weight. Genetic factors can contribute to variations in BMI among different individuals.
- Age: BMI tends to evolve over the course of one’s life. It typically increases with age, and this natural progression should be considered when evaluating BMI.
- Hormonal Influences: Hormones are key players in the regulation of metabolism and body composition. Imbalances in hormonal levels can lead to weight fluctuations, thereby impacting BMI.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Socioeconomic status can influence access to healthy foods and opportunities for physical activity, contributing to BMI disparities among diverse population groups.
- Psychological Factors: Emotional and psychological factors, such as stress, depression, and eating behaviors, exert a significant influence on BMI by shaping eating patterns and physical activity levels.
- Environmental Factors: Access to healthy food options and neighborhood safety are environmental factors that can affect BMI by influencing individuals’ lifestyle choices.
- Medications and Health Conditions: Certain medications and underlying health conditions may lead to fluctuations in weight and BMI. Evaluating these factors is crucial when assessing BMI accurately.
In conclusion, BMI is a multifaceted metric shaped by a plethora of internal and external factors. A comprehensive understanding of these factors empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and take proactive steps towards achieving or sustaining a healthy BMI.
Unlocking the Path to Height Growth and Long-Term Well-being
In the quest for achieving and maintaining a healthy Body Mass Index (BMI), it is essential to shift our perspective towards holistic well-being. Rather than simply focusing on shedding excess weight, let’s explore a comprehensive guide to help you not only reach your ideal height but also sustain it for the long haul:
- Embrace a Well-Rounded Fitness Routine: Incorporating regular physical activity is key to height growth and overall health. Engage in a diverse exercise regimen that includes aerobic workouts, strength training, and participation in sports. This proactive approach not only aids in managing BMI but also fortifies your overall well-being.
- Nourish Your Body with a Balanced Diet: Opt for a nutritionally diverse diet that includes an abundance of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. This dietary approach supports optimal height growth while providing your body with essential nutrients for overall vitality.
- Mindful Eating and Portion Management: Cultivate mindfulness around your eating habits. Take time to savor each bite and be aware of your food consumption. Avoid overindulgence by monitoring portion sizes. This approach not only contributes to healthy height growth but also fosters a positive relationship with food.
- Prioritize Restorative Sleep: The importance of adequate sleep cannot be overstated. It directly impacts your ability to achieve and maintain a healthy height. Ensure you get sufficient sleep, as it is a vital element in the journey towards reaching your height goals.
- Holistic Stress Management: Stress can be a significant obstacle to height growth. Incorporate stress management strategies such as meditation, yoga, or engaging in enjoyable hobbies. Effectively dealing with stress is essential for preventing fluctuations in height and supporting long-term growth.
Unveiling the Truth about Height Growth and Understanding Its Complexities
While height growth is a crucial aspect of our well-being, it’s important to dispel common misconceptions and acknowledge the intricacies involved:
- Genetic Factors: Genetics play a significant role in determining your ultimate height potential. While lifestyle factors can influence your growth to some extent, genetics lay the foundation for your height.
- Nutrition and Hormones: Proper nutrition during childhood and adolescence is vital for maximizing height potential. Growth hormone production, influenced by factors like sleep and nutrition, also plays a pivotal role in determining your final height.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental factors, such as exposure to adequate nutrition, a healthy living environment, and access to healthcare, can impact height growth, especially during crucial growth periods in childhood and adolescence.
In conclusion, the journey to achieving and maintaining a healthy height should encompass a holistic approach to overall well-being. By focusing on fitness, nutrition, mindful eating, quality sleep, and stress management, you can not only reach your height goals but also enjoy a healthier, happier life. Furthermore, understanding the genetic and environmental factors at play in height growth provides a more comprehensive perspective on this intricate aspect of our well-being.
The Consequences of Elevated BMI:
A high Body Mass Index (BMI) can have far-reaching consequences that impact both health and appearance. It’s no surprise that individuals with excess weight or obesity may experience a decline in self-confidence when it comes to their attire, social activities, and overall well-being.
Furthermore, having a high BMI places individuals at an increased risk of serious health conditions, including:
- Cardiovascular Issues: Elevated BMI is associated with a higher likelihood of heart disease, hypertension, and related complications.
- Metabolic Disorders: Conditions such as diabetes and fatty liver disease are more prevalent among those with high BMI.
- Cholesterol Imbalances: High cholesterol levels often accompany obesity, increasing the risk of heart problems.
- Gallbladder Disease: Obesity can contribute to the development of gallstones and related issues.
- Musculoskeletal Problems: Excess weight can strain the bones and joints, leading to conditions like osteoarthritis.
In conclusion, this article has delved into the factors influencing changes in body weight and the repercussions of an elevated BMI. It underscores the importance of monitoring your BMI and engaging in physical activities such as going to the gym, practicing yoga, or incorporating simple exercises into your routine to help maintain a healthy weight and optimize overall health.
Conclusion
The Body Mass Index (BMI) stands as a commonly employed and valuable metric for gauging the intricate interplay of weight and height within an individual’s physique. Derived from a straightforward mathematical formula, this metric furnishes a preliminary insight into the distribution of body fat and aids in ascertaining an individual’s placement within the spectrum encompassing underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. Sustaining a well-balanced BMI holds paramount significance in safeguarding overall well-being and mitigating the peril of chronic maladies. Nevertheless, it is imperative to recognize that BMI should be integrated into a holistic assessment of one’s health, interwoven with discerning considerations of lifestyle choices and broader health evaluations.
FAQs
Can BMI be inaccurate for athletes or individuals with high muscle mass?
Yes, BMI may be less accurate for individuals with high muscle mass, as it does not differentiate between fat mass and muscle mass. Such individuals may have a higher BMI due to increased muscle weight.
Can BMI alone determine if someone is healthy or unhealthy?
No, BMI should not be the sole determinant of health. Other factors, such as blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall fitness, should be considered for a comprehensive evaluation of an individual’s health.
Is a high BMI always indicative of poor health?
While a high BMI can be associated with increased health risks, it is not always indicative of poor health. Factors such as body composition, distribution of fat, and overall fitness should also be considered.
Can BMI be used for children and adolescents?
Yes, BMI can be used for children and adolescents. However, the interpretation of BMI results may differ for different age groups, and percentiles are used to assess weight status in relation to age and gender.
How can I maintain a healthy BMI?
Maintaining a healthy BMI involves adopting a balanced lifestyle. Engage in regular physical activity, follow a nutritious diet, practice portion control, get sufficient sleep, and manage stress effectively to support overall health and weight management.
- Related post: Top 14 ways to increase height at the age of 16

